
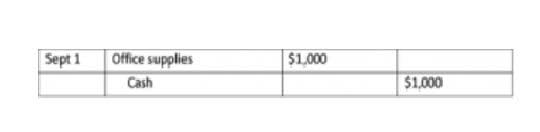
It’s important to note that if the business uses the ABC system, the individual activity is absorbed on a specific basis. For instance, cleaning and maintenance expenses will be absorbed on the basis of the square feet as shown in the table above. If the absorbed cost is more than the actual cost, an adjusting entry is passed to reduce the expenses.
- To tackle this problem predetermined overhead rates are used instead of actual overhead rates.
- For these reasons, most companies use predetermined overhead rates rather than actual overhead rates in their cost accounting systems.
- Fixed overheads are expected to increase/decrease per unit in line with the seasonal variations.
- Overhead rates refer to the allocation of indirect costs to the production of goods or services.
Income Statement Under Absorption Costing? (All You Need to Know)

The computation of the overhead cost per unit for all of the products is shown in Figure 6.4. One more approach is to calculate the plantwide overhead rate using an alternative approach or direct cost method. To calculate this, we first need to identify the total direct cost of production and the total overhead cost for the specific period. Thus, this total overhead is divided by the total direct cost predetermined overhead rate formula to ascertain the single plantwide overhead rate.

Ethical Cost Modeling
Cut unnecessary spending – Review budgets to identify and eliminate expenses that do not contribute real business value. Discover essential eBay selling tools, including seller, marketing, and listing tools to enhance your ecommerce business efficiency and increase sales. One common way to adjust for over or under-absorption is to adjust your cost Accounts Receivable Outsourcing of goods sold for the difference.
Unit Converter
The management can estimate its overhead costs to be $7,500 and include them in the total bid price. The Predetermined Overhead Rate Formula is a finance and accounting term that is used to allocate estimated manufacturing overhead costs to products or jobs. It’s formulated by dividing estimated overhead costs by some measure of estimated total output such as direct labor-hours or machine-hours. This rate is typically established before a period begins and helps companies to estimate costs more accurately.
How to Calculate Predetermined Overhead Rate (With Examples)
Fixed costs are those that remain the same even when production or sales volume changes. So if your business is selling more products, you’ll still be paying the same amount in rent. But before we dive deeper into calculating predetermined overhead, we need to understand the concept of overhead itself. Two companies, ABC company, and XYZ company are competing to get a massive order that will make them much recognized in the market. This project is going to be lucrative for both companies but after going over the terms and conditions of the bidding, it is stated that the bid would be based on the overhead rate. This means that since the project would involve more overheads, the company with the lower overhead rate shall be awarded the auction winner.
The key is to select an allocation base that has a logical relationship with your overhead costs. If you pick an online bookkeeping allocation base that doesn’t actually correlate with how overhead costs are incurred, your product costs will be distorted. For example, if you use direct labor hours but most of your overhead costs relate to running machines, you’ll miscalculate.
That is, the company is now aware that a 5-hour job, for instance, will have an estimated overhead cost of $100. The predetermined overhead rate formula can be used to balance expenses with production costs and sales. For businesses in manufacturing, establishing and monitoring an overhead rate can help keep expenses proportional to production volumes and sales. It can help manufacturers know when to review their spending more closely, in order to protect their business’s profit margins. A predetermined overhead rate is used by businesses to absorb the indirect cost in the cost card of the business. Further, this rate is calculated by dividing budgeted overheads by the budgeted level of activity.
- Overhead costs encompass all indirect manufacturing costs that are not direct materials or direct labor.
- Thus the organization gets a clear idea of the expenses allocated and the expected profits during the year.
- Dividing expenses by operating and overhead help to set prices accordingly and increase profit margins.
- Once the units to be produced or activity base has been estimated, the business must then estimate its total manufacturing costs based on the number of units to be produced.
- It’s a good way to close your books quickly, since you don’t have to compile actual manufacturing overhead costs when you get to the end of the period.
- A clear understanding of these concepts is essential for accurately calculating and applying overhead costs to products or services.
What are some examples of overhead costs?
And because overhead rates are an estimate, if the numbers you’re accessing to calculate your overhead rate aren’t accurate, then the results will be inaccurate as well. Predetermined overhead rates are applied in various financial and operational areas. Carefully minimizing overhead is crucial for small businesses to maintain profitability.

The overhead rate for the molding department is computed by taking the estimated manufacturing overhead cost and dividing it by the estimated machine hours. The companies use different allocation bases when calculating their predetermined overhead rates. At the start of 2021, Dorothy’s Hat Company estimated that the total manufacturing overhead cost for the year would be $320,000, and the total machine hours would be 50,000 hours.

